subtle indicators
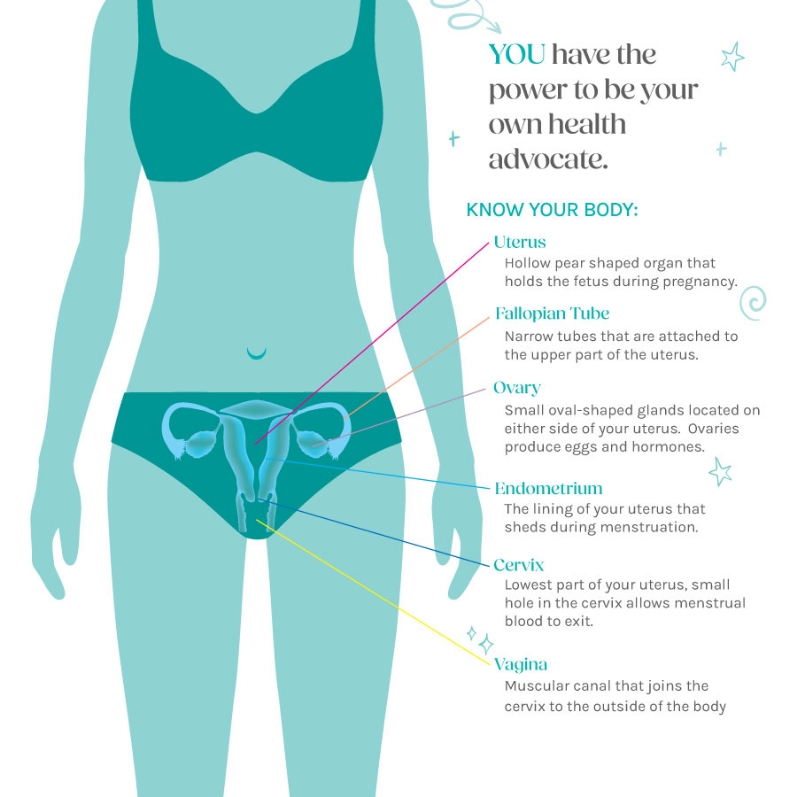
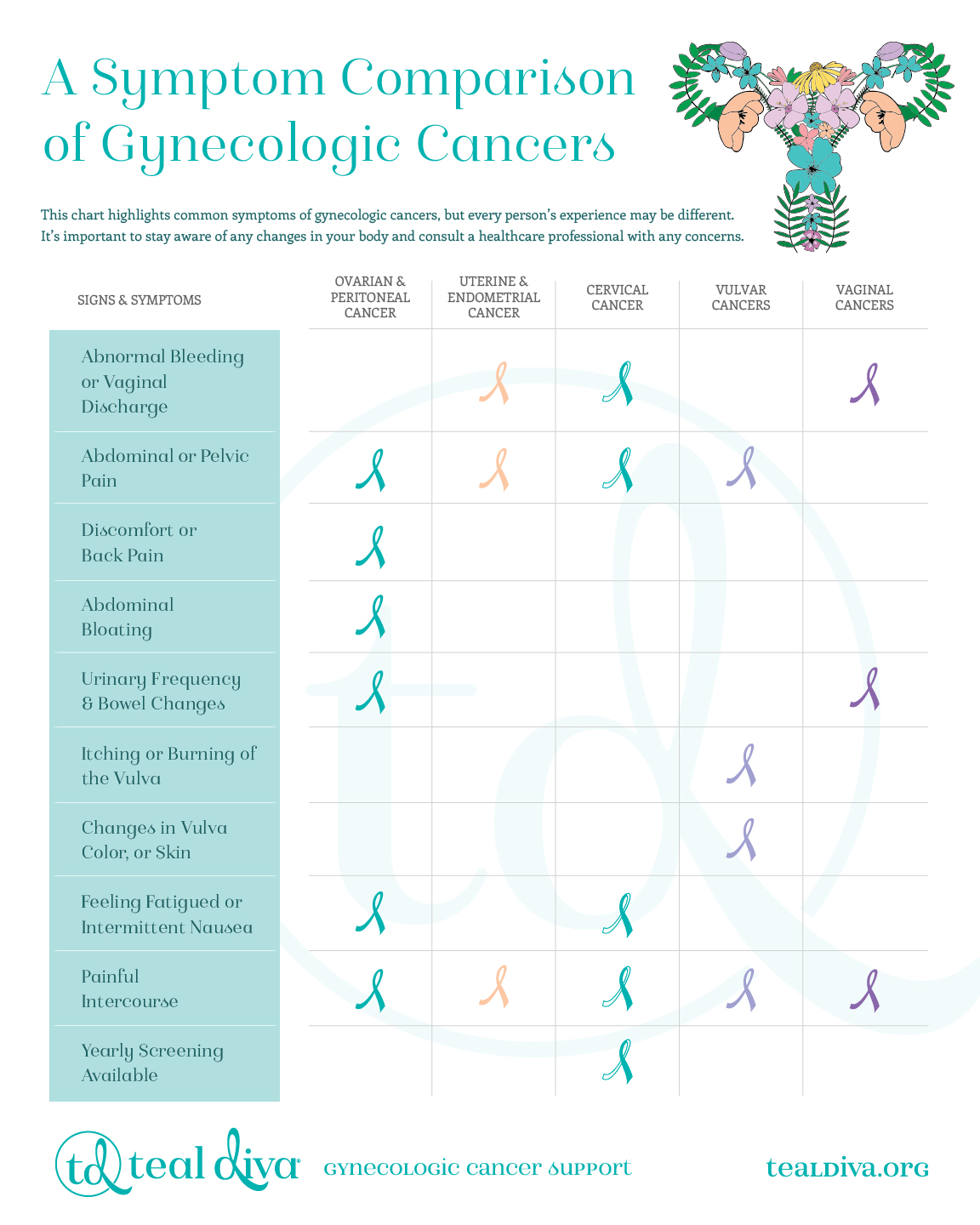
Gynecologic cancers are a group of cancers that originate in the female reproductive organs at any age. Symptoms can include:
- Bloating or feeling full quickly
- Difficulty eating
- Back pain
- Pain or pressure in pelvis or abdomen
- Constipation or change in bowel habits
- Frequent or urgent urination
- Fatigue
- Discomfort during intercourse
- Menstrual irregularities
While these symptoms may not exclusively indicate gynecologic cancer, if they persist daily for several weeks, it’s crucial to seek guidance from a gynecologist.